AAPOD2 Image Archives
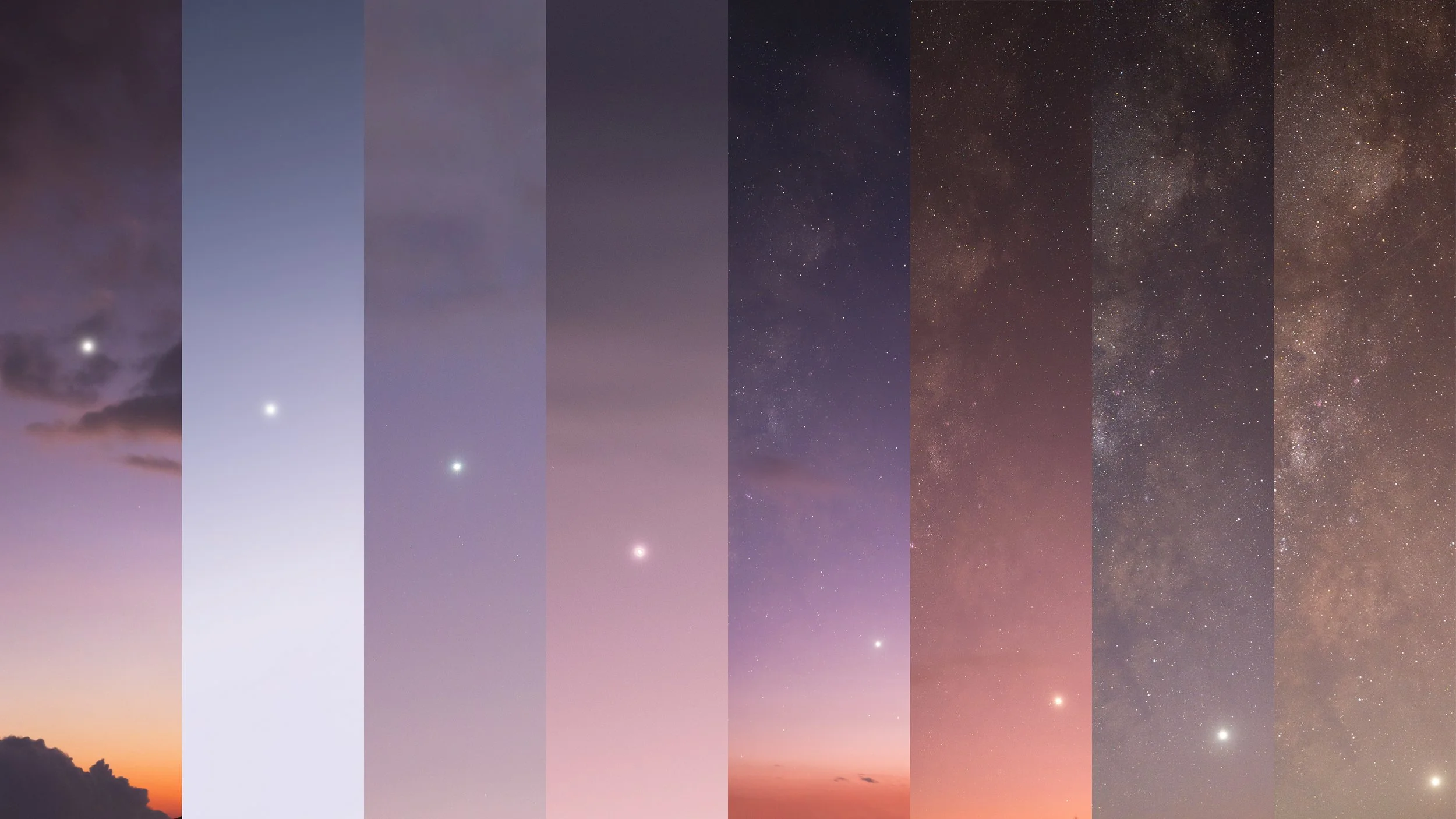
Venus through Twilight Colors
The transition from twilight to night is depicted, spanning approximately 26 minutes at this latitude.
This image is a combination of photographs taken over three days—October 30, October 31, and November 2.
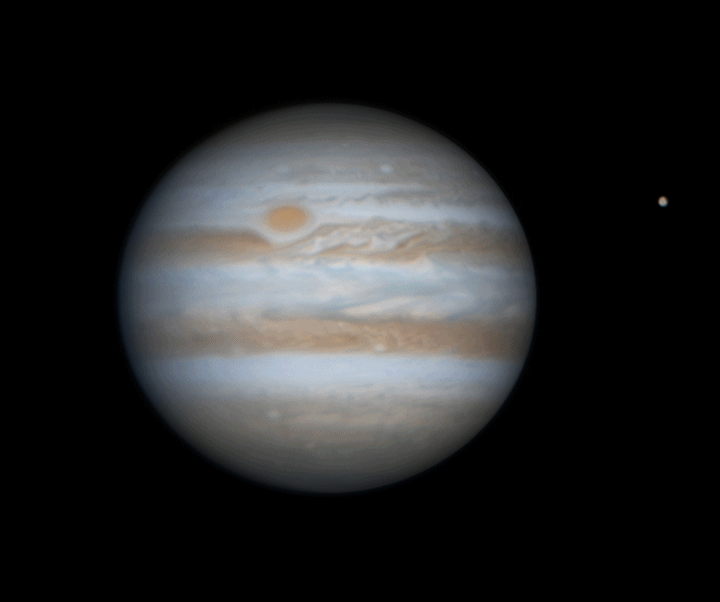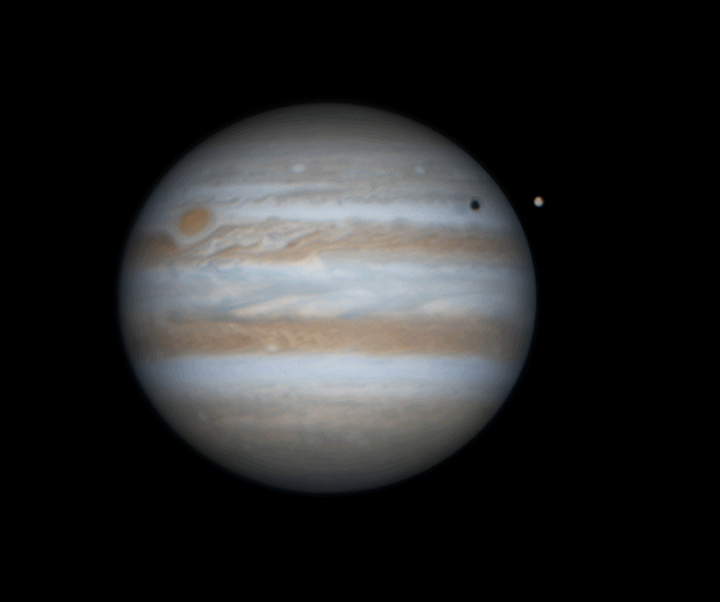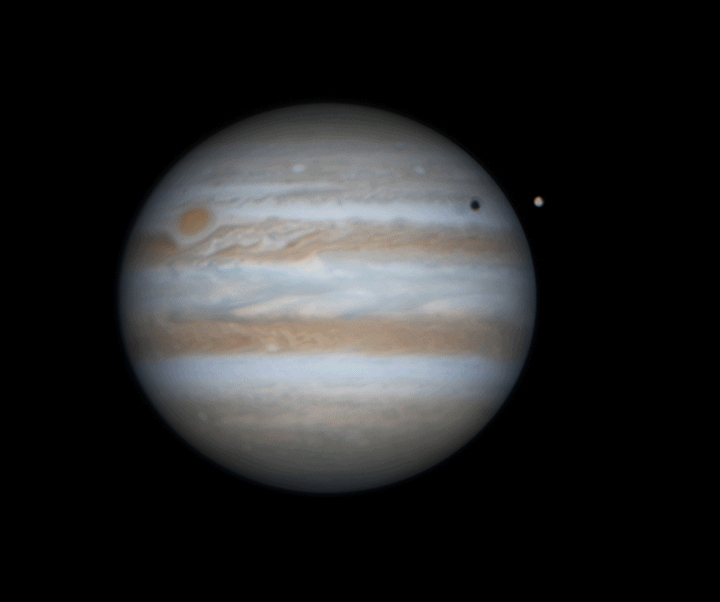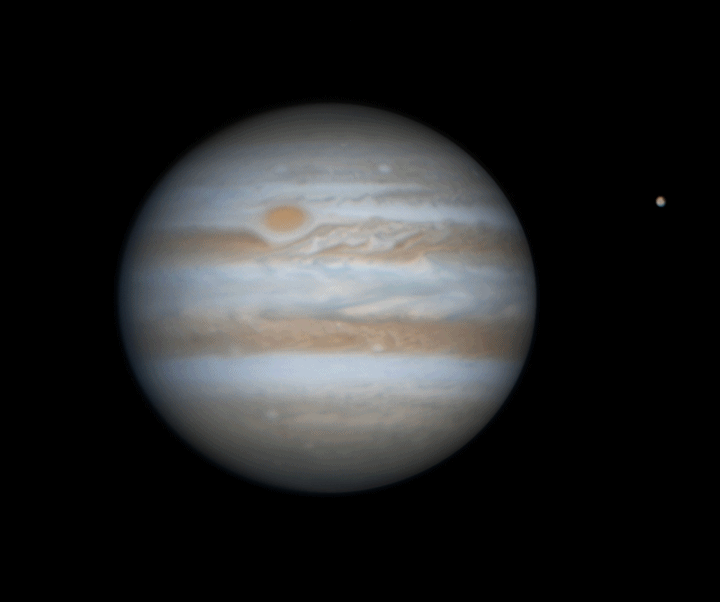
Jupiter rotation
Watching the planets rotate is always a captivating experience, but with Jupiter, it becomes truly spectacular. The largest planet in our Solar System completes a full rotation on its axis in just 10 hours, creating a mesmerizing display of motion. In this animation, we witness Jupiter's moon Europa passing in front of the gas giant, accompanied by the shadow it casts across the planet's swirling cloud tops. The striking 3D effect as Europa crosses Jupiter's face adds an incredible sense of depth and realism, making this celestial event even more awe-inspiring.
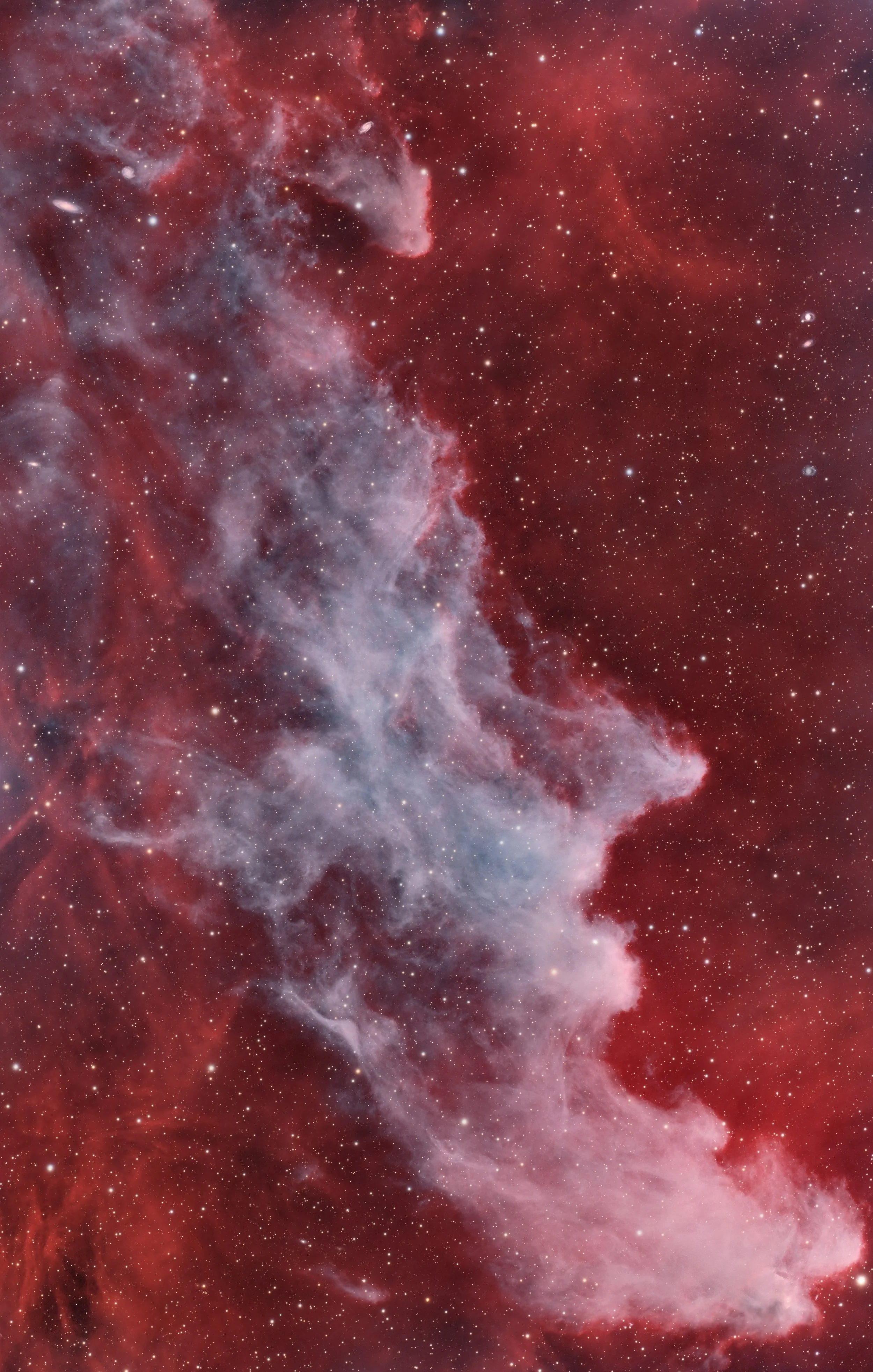
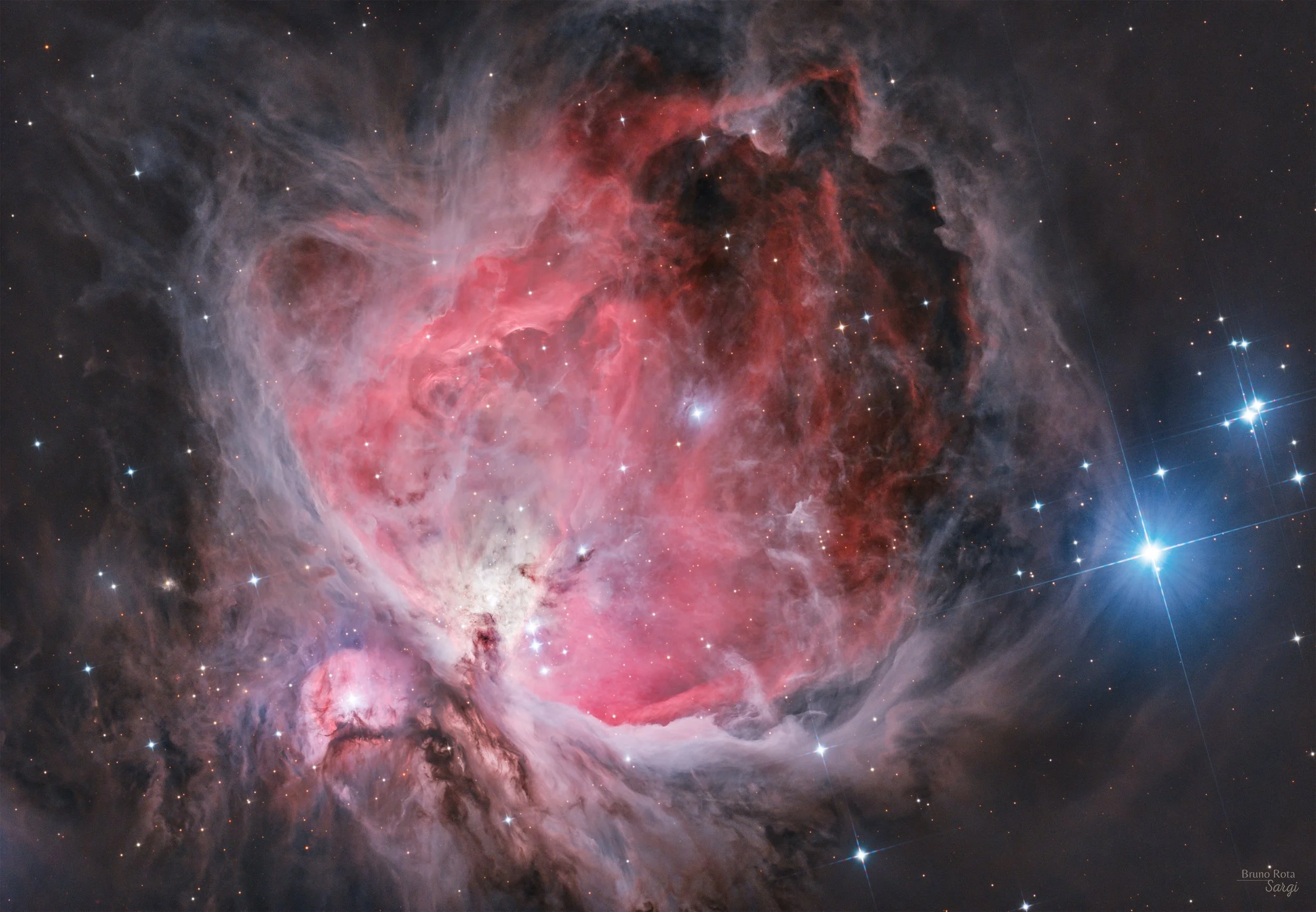
IC434 - Dusty Region around the Horse Head Nebula
This image highlights the Horsehead Nebula (Barnard 33) and its surrounding dusty region, set against the glowing backdrop of IC 434 in the constellation Orion.
The Horsehead Nebula, one of the most iconic dark nebulae in the night sky, is silhouetted against the bright hydrogen-alpha emissions of IC 434. Its distinctive shape is sculpted by powerful stellar winds and intense radiation from nearby stars, including Alnitak, the easternmost star of Orion’s Belt, which lies just outside the frame.
This dusty region is rich in interstellar material, with dark lanes of cold molecular gas and dust weaving through the glowing emission nebula. The complex interplay of light and shadow creates a dramatic and textured view of this stellar nursery, where new stars are forming deep within the clouds.
The region lies approximately 1,500 light-years away and spans a vast area of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. This detailed portrait captures the beauty of cosmic creation, offering a glimpse into the processes shaping our galaxy.
IC 410
This image captures IC 410, also known as the Tadpole Nebula, located in the constellation Auriga. A glowing region of ionized hydrogen, this emission nebula surrounds the open star cluster NGC 1893, a young cluster whose stars power the nebula's illumination.
The "tadpoles" themselves—two dense, dusty structures stretching roughly 10 light-years each—are regions of concentrated gas and dust, shaped by stellar winds and radiation. These structures are likely sites of ongoing star formation, hidden within their dense cocoons.
The image displays a rich palette of colors, showcasing hydrogen-alpha (red), oxygen (blue), and sulfur (gold) emissions, bringing out the intricate textures and dramatic interplay of light and shadow within the nebula.
IC 410 resides approximately 12,000 light-years away and spans about 100 light-years across. This vibrant celestial portrait reveals the complex dynamics of star formation and the incredible power of young, massive stars.
Jones-Emberson 1
Captured from a backyard observatory in Romano d’Ezzelino, Italy, under the light-polluted Bortle 7/8 skies, this image showcases Jones-Emberson 1 (PK 164+31.1), a faint planetary nebula located approximately 1,600 light-years away in the constellation Lynx. Nicknamed the "Headphone Nebula" due to its distinctive shape, this relic of a dying star’s outer layers appears as a delicate bubble of ionized gas, glowing faintly against the backdrop of space.
The nebula, around four light-years across, is a testament to the star's final stages of life. At its heart lies a fading white dwarf, the exposed core of the progenitor star that has shed its outer layers. The intricate structure and subtle colors in the nebula result from the interaction of ultraviolet radiation from the white dwarf with the surrounding gas, causing it to fluoresce in blues and greens, particularly in oxygen emission lines.
Imaging this elusive object from a bright suburban sky was a challenge, but careful planning and advanced post-processing brought its delicate features to life. Despite the light pollution, the faint circular shell and central star are clearly resolved, a testament to the dedication and skill of the astrophotographer.
Fun Fact: Jones-Emberson 1 was first cataloged in 1939 by R.C. Jones and R.A. Emberson. Unlike more famous planetary nebulae like the Ring or Dumbbell Nebula, it remains a lesser-known gem, often eluding amateur astronomers due to its low surface brightness.
Les fantômes de Cassiopée (The Ghosts of Cassiopeia)
The Ghosts of Cassiopeia, also known as IC 63, is a faint, ethereal nebula located approximately 550 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia. This nebula is illuminated and sculpted by the nearby blue supergiant star Gamma Cassiopeiae, which is a variable star more than 34,000 times as luminous as the Sun. The intense radiation from Gamma Cassiopeiae causes the hydrogen gas in the nebula to glow red, while its ultraviolet radiation sculpts and slowly erodes the nebula over time.
Interestingly, IC 63 is part of a larger complex of nebulosity surrounding Gamma Cassiopeiae, making it a fascinating target for both astrophotography and scientific study of star-forming regions.
The Diamonds of Bogenfels
Location (was image taken with remote scope?): Namibia.
Image Description and Details: The mining ghost town of Bogenfels lies in the Sperrgebiet in South West Namibia. Sperrgebiet translated from German means the restricted area. The Sperrgebiet is an active diamond mining zone and one risks getting shot if not having the proper credentials and permits to enter the area. In times past the German colonizers had set up diamond mining towns and what we see here is a decrepit washing plant in which diamonds were separated from the soil they were excavated from. The diamonds on the ground are since long gone but the ones in the skies above, remain.
Resolved in the sky we see clockwise, from the Pleiades Star Cluster to the Taurus asterism with its dust clouds, and on to the Witch head Nebula. The distinctive Orion Molecular complex with the Horsehead nebula and the Barnard’s loop take center stage.
The Seagull Nebula appears further right before we loop back to the Rosette and Christmas tree Nebula and onward to the Flaming star Nebula before completing the circle at the California Nebula. Whew!
LDN 1251 - LDN 1247 THE ROTTEN FISH NEBULA
NGC 5189, also known as the Rotten Fish Nebula, is a striking planetary nebula located about 3,000 light-years away in the constellation Musca. Its name comes from its unusual, fish-like shape, with twisted lobes resembling a decaying skeleton. Unlike many planetary nebulae, NGC 5189 has a complex, asymmetrical structure, possibly shaped by magnetic fields, rotation, or interactions with a companion star. This makes it one of the more intricate and visually captivating nebulae. The nebula is formed by the ejected outer layers of a dying star, now a hot white dwarf, which ionizes the surrounding gas, causing it to glow.
Despite its vast size of 2,000 light-years across, the Rotten Fish Nebula remains faint and requires telescopic observation. It resides in the Musca star-forming region, an area rich in young stars and gas, highlighting the contrast between the ongoing stellar activity around it and the aging star at its core. NGC 5189 provides valuable insights into the final stages of stellar evolution and the processes behind the formation of planetary nebulae.
Centaurus A: Extreme Deep Field - 321 Hours
This ultra-deep, high-resolution image of Centaurus A (NGC 5128) was created using data collected over ten years, from 2013 to 2024, with my homebuilt telescope. There are no stars in this image — every single point of light is either part of the Centaurus A system or a distant background galaxy or quasar!
This work is a continuation of my Centaurus A "Extreme Deep Field" project, now with a larger field of view (FOV) and significantly more data — 321 hours in total, including 126 hours of narrowband H-Alpha and OIII.
In 2013 I gathered 120 hours of data on Centaurus A and processed the then deepest image ever obtained of this magnificent galaxy, showing several structures not revealed by amateurs before. I updated and re-processed the image in 2014 and 2018, including adding H-Alpha data to highlight the impressive emission structures triggered by the relativistic jet from the supermassive central black hole. This current image is a major update, now just over 10 years after my initial ultra-deep image was completed.
Several unique features are visible:
The full extent of H-Alpha and OIII filaments associated with the relativistic black hole jets:
The inner and outer Northern (bottom) jet shows many faint details not previously imaged
The Southern (top) jet is visible as a small red blob in the 10 o'clock position (first detected optically in my earlier 2013 image)
The complete shell structure of the halo, showing both the faint outer shells and brighter inner ones
A distinct blue arc, a remnant stellar stream from a dwarf galaxy absorbed by Centaurus A
1108 of the known globular clusters orbiting the galaxy
Countless distant background galaxies and quasars
Perseids 2024 maximum
This breathtaking mosaic showcases the pinnacle of the Perseid meteor shower at its peak from August 12th to 13th, alongside meteors captured over five consecutive nights between August 8th and 13th. To craft this cosmic masterpiece, an astonishing 14,000 frames were recorded across five photographic setups, with approximately 150 meteor trails carefully selected for inclusion.
Adding to the celestial wonder, the image also features the ethereal aurora borealis glowing in dynamic green and purple hues, complemented by the extremely rare Stable Auroral Red (SAR) arc—a phenomenon rarely seen or photographed. Unlike traditional auroras, SAR arcs appear as faint, stable, reddish arcs caused by low-energy electrons interacting with the ionosphere, far above the Earth's surface. This makes their inclusion in this mosaic an extraordinary achievement.
The mosaic also captures the serene beauty near Śnieżnik’s rugged mountainous landscapes under pristine dark skies, highlighting the interplay between Earth’s natural wonders and the cosmic spectacle above.
What Fortunes Do You See Gazing into the Crystal Ball Nebula (NGC1514)
The Crystal Ball Nebula (NGC 1514), located in the constellation Taurus, is a mesmerizing planetary nebula formed from the ejected outer layers of a dying star. At its heart lies a binary star system, with the central star—a bright, hot white dwarf—illuminating the surrounding shells of gas and creating the nebula's ethereal glow.
What makes NGC 1514 particularly striking is its unique appearance: instead of the typical spherical shape of many planetary nebulae, it exhibits a complex structure of overlapping shells and filaments. These features result from the interactions between the stellar winds of the central stars and the surrounding interstellar medium.
The Witch Head Nebulae
The Witch Head Nebula (IC 2118), a faint reflection nebula situated in the constellation Eridanus, reveals its ghostly visage in this exceptional capture. Located approximately 900 light-years from Earth, the nebula’s distinctive shape resembles the profile of a cackling witch, a fitting tribute to its name. This cosmic apparition glows due to starlight reflected off interstellar dust, primarily illuminated by the nearby supergiant star Rigel in the constellation Orion.
The nebula’s bluish hues are a result of light scattering—shorter blue wavelengths are scattered more efficiently by the dust particles, a phenomenon similar to why Earth’s sky appears blue. Surrounding the Witch Head are subtle wisps of molecular clouds, hinting at the nebula’s dynamic and evolving environment.
Captured from the pristine skies of the Atacama Desert, this image takes full advantage of the location’s Bortle 1 conditions, highlighting the intricate textures and delicate structures of this elusive celestial object.
The Witch Head Nebula stands as a stunning reminder of the interstellar artistry woven into the fabric of our universe, showcasing the interplay of starlight and dust against the backdrop of infinite space.
Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex
Captured from the pristine dark skies of Tivoli Astrofarm in Namibia, this stunning image of the Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex showcases one of the most colorful and dynamic regions of the night sky. Located at an estimated distance of about 140 parsecs (460 light-years), this interstellar masterpiece is among the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System.
This complex hosts a variety of nebulae, including emission, reflection, and dark nebulae, creating a vibrant interplay of colors and textures. The golden hues surrounding Antares, the heart of the constellation Scorpius, contrast with the electric blue of reflection nebulae and the inky black of dark clouds, highlighting the diverse cosmic phenomena within this region.
To achieve this breathtaking composition, the photographer combined data from two focal lengths, each meticulously capturing this field for 3 hours. The layering of perspectives allows for an exquisite balance of resolution and field of view, bringing out intricate details in the dust lanes and the subtle glow of starlight scattered by cosmic particles.
The Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex is a celestial jewel box, revealing the beauty of stellar nurseries and the interplay of light, dust, and gas that shape the galaxy. Observing and imaging this region is a dream for astronomers and astrophotographers alike, offering a vivid window into the wonders of the universe.
LBN 777 - The Baby Eagle Nebula
Nestled within the Taurus Molecular Cloud, LBN 777, also affectionately called the Baby Eagle Nebula, is a stunning interplay of reflection and dark nebulae located approximately 450 light-years away. Its delicate, sweeping arcs of dust and faintly glowing regions evoke the image of a young eagle with its wings partially spread, soaring quietly through interstellar space.
This nebula is part of a larger complex of molecular clouds in Taurus, a region renowned for active star formation. The faint glow visible in the nebula comes from starlight scattered off fine dust grains, while darker regions obscure the light from stars beyond, creating a striking contrast. The intricate shapes within LBN 777 owe their origin to the turbulent forces of stellar winds, radiation pressure, and gravity that sculpt the dust and gas into intricate structures.
Photographing this elusive target requires patience and skill, as its faint features demand long exposure times under dark skies. Using broadband filters to capture the reflection components and narrowband techniques to emphasize subtle hydrogen emissions helps bring out the nebula’s texture and depth.
The Baby Eagle Nebula is a quiet but poignant reminder of the cosmic forces at work in our galaxy. Its beauty lies in its understated elegance, captivating the imagination of those who seek its faint wings in the night sky.
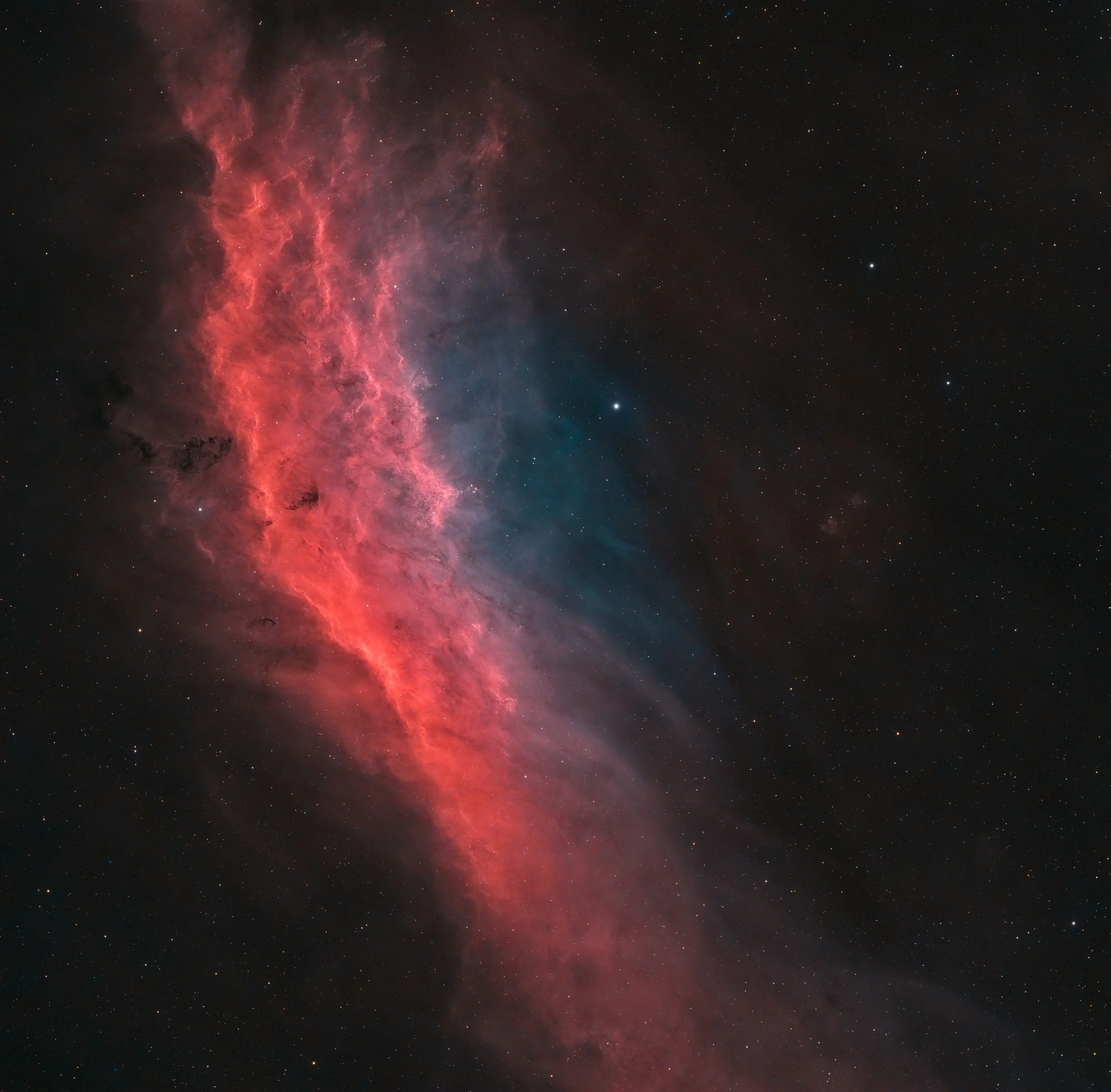
The California Nebula
The California Nebula, named for its resemblance to the shape of the U.S. state, is an iconic emission nebula located in the constellation Perseus, about 1,000 light-years away. Spanning nearly 100 light-years, this massive cloud of ionized hydrogen glows predominantly in deep red hues due to the influence of nearby star Xi Persei, an exceptionally hot and bright O-type star. The intense ultraviolet radiation from Xi Persei energizes the nebula's hydrogen gas, causing it to emit the characteristic red light of H-alpha.
This nebula is particularly intriguing because of its elongated structure and dynamic interplay of light and shadow, created by regions of interstellar dust that obscure parts of its glowing gas. It’s an active region of the sky, rich with complex textures and fine details that are brought to life in narrowband imaging, especially with H-alpha filters.
Astrophotographers and astronomers alike are drawn to the California Nebula for its striking appearance and its position within a star-rich field of the Milky Way. Although faint to the naked eye, it is a treasure for imaging enthusiasts who can reveal its full splendor under dark skies with long exposures.
A celestial homage to Earth’s own geography, the California Nebula is a timeless subject that captures the imagination and beauty of the universe.